End to End Neural Art with Generative Models
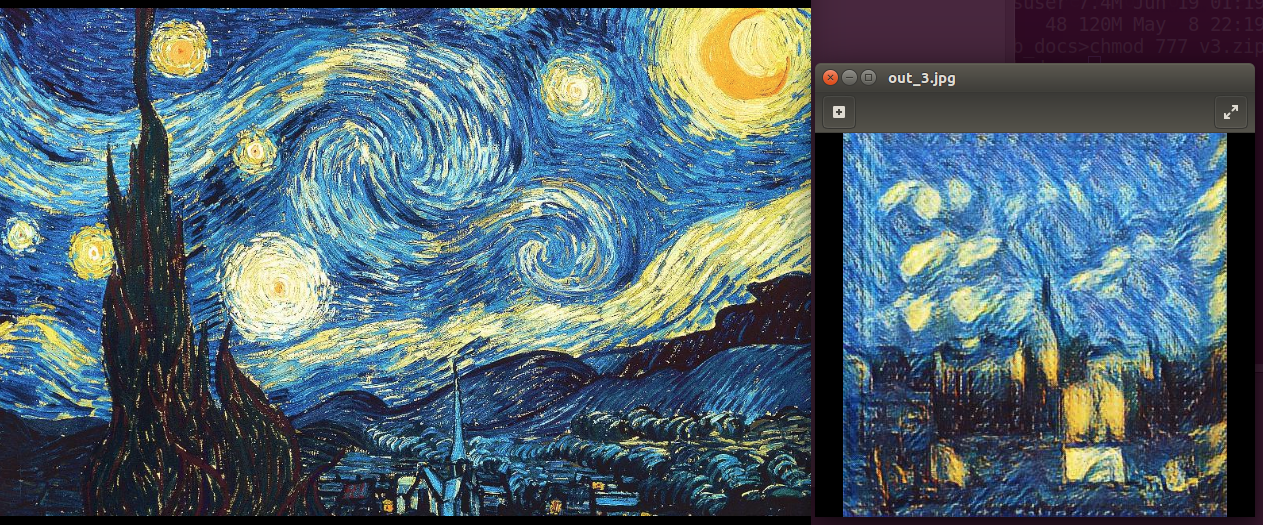
In this blog, we will describe how we design an end to end neural starry night style generator: Compare to traditional optimization based neural style algorithm, this end to end generator will generate styled image in a single shot, which makes it possible to generate style in real time.
Note: It is an independent work along with [6]. Thanks Ian Goodfellow for pointing out this.
Implementation is available at https://github.com/dmlc/mxnet/tree/master/example/neural-style based on MXNet. These models can be deployed to JavaScript based browser client and mobile phone directly. We will release multi-GPU version soon.
A pretrained model is avaliable at https://github.com/dmlc/web-data/raw/master/mxnet/art/model.zip
Background
The standard neural style algorithm [1] is based on this idea: We define two L2 loss: content loss and style loss, then use VGG network to extract features of content images and style images. Then given a random initialized image, use VGG network extract feature, calculate content loss and style loss, then use gradient of data to update the image. After repeating hundreds of this process, we can finally get an image mixture content and style. A MXNet implementation can be found at: https://github.com/dmlc/mxnet/tree/master/example/neural-style
The problem for optimization based algorithm is speed. For example, for a single on advanced GPU, it will takes minutes for computation. On some online service, users even need to wait for weeks for a result.
Inspired by generative model, especially generative adversarial network (GAN) [2], we design a generative model for neural style. To simplify the problem, current version only support one style: starry night by Van Gogh.
An End to End Neural Style Network
In neural style algorithm, the gradient of data is used to update the input image. However in GAN, gradient of data from discriminator is used to update generator. Inspired by this, we design a generator, which is using gradient of data to update a network.
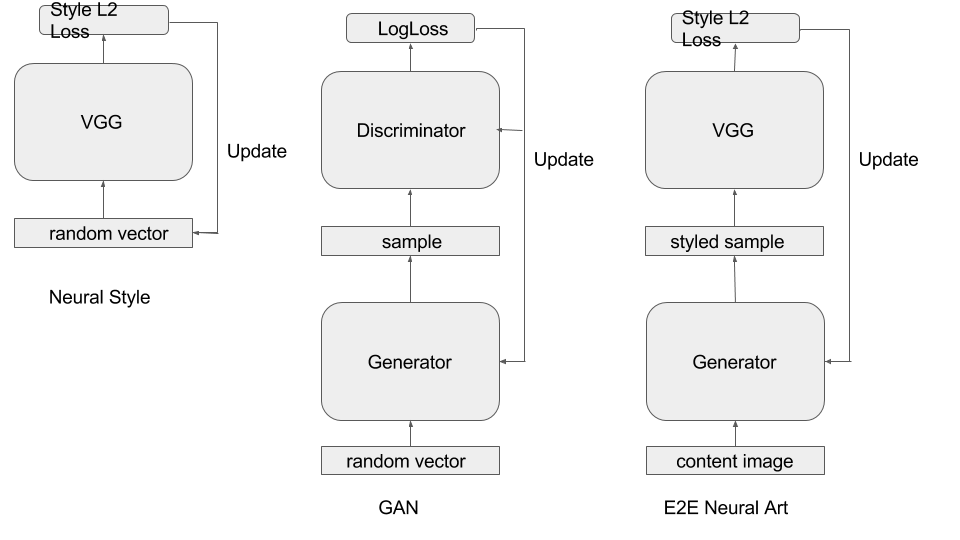
The relation of neural style, GAN, and End to end neural art has been shown in figure above.
Boosting Generator’s quality
However, the architecture above will not guarantee a you good result. For example, a sample output of a Deconvolution generator with Residual connection (commonly used in GAN) is like:
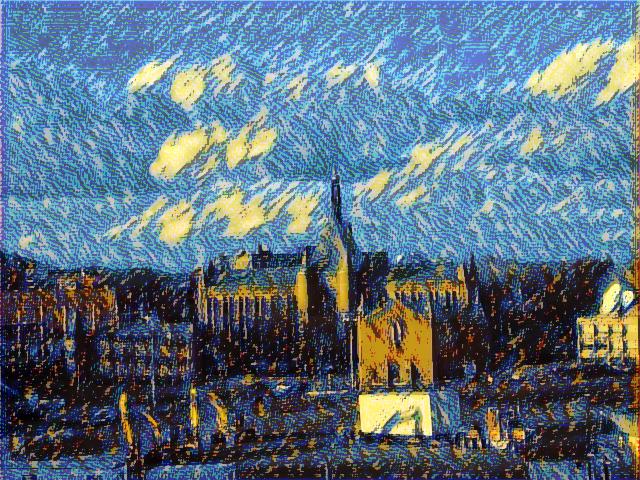

We developed a bunch of techniques to improve generator quality:
- Residual Connection
- Pure Convolution generator
- “Boosting” of generators
Residual connection in End to End Neural Art doesn’t mean same to original residual connection [3]. There is weight in residual connection, which will make a balance in input data and generated result.
Instead of using many Deconvolution layers in generator, we use a pure convolution generator. In this problem, the feature map in convolution generator doesn’t change. This kind of generator will preserve more information on input.
The third technique “boosting” is the most important one to improve the quality. The idea is the next generator should generate based on previous generator’s result. This additive training process magically improves quality of result. The following 4 images comes from 4 generators in a line:
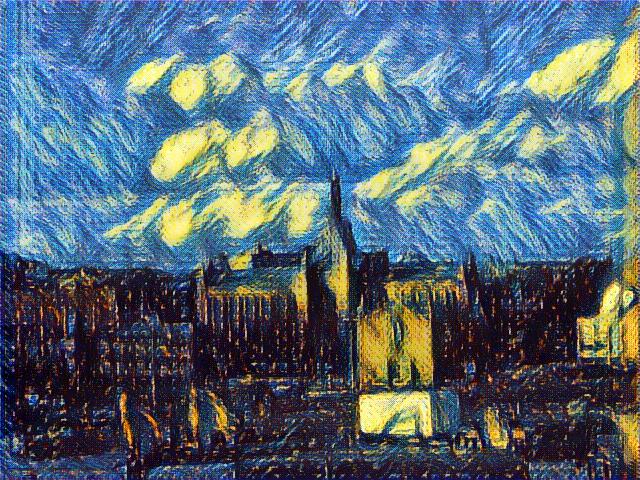
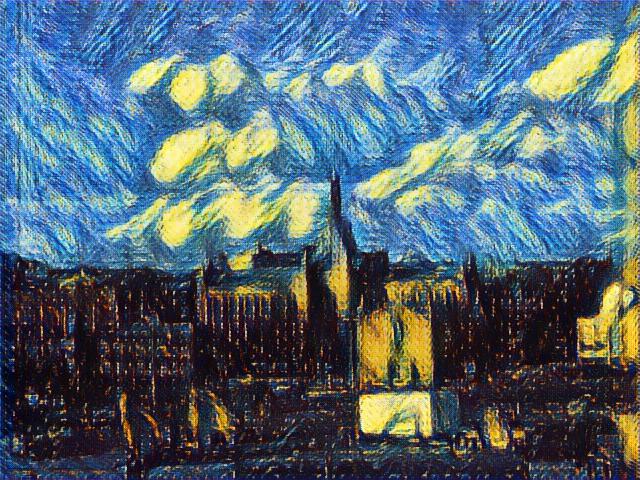
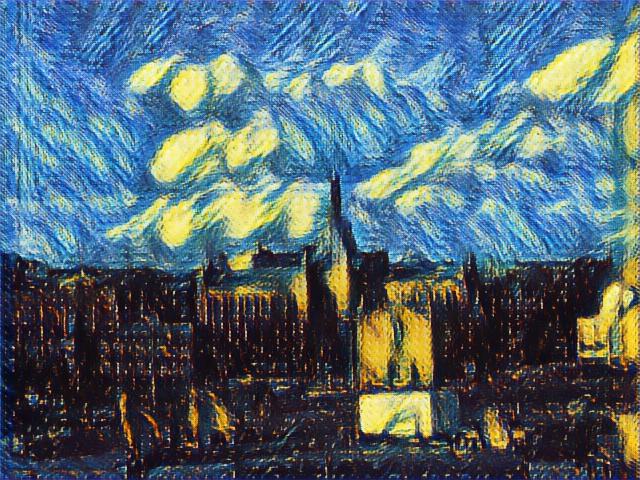




Note: If we choose to share weight of different generators, it will become structure in [4]. If we choose to propagate gradient between generators, the structure will become structure similar in [5]. Moreover, the residual connection in single generator will result in an ensemble of generators in final output.
We choose to not sharing weight between these generators, this allows us to enable different kind of generator structure at each stage. For these samples, the first and last generator are convolution generator and the middle two are deconvolution generators.
Training
The training data is 26k images sampled from MIT Place dataset. The code is using MXNet new module API. The pretrained model is trained with 2 epoch.
Further work
- We didn’t turn any parameters on these generators. There is A LOT of space to improve generator’s structure and training.
- Expanding the training dataset will be helpful for various of input. Current model is good on buildings, basically it is trained on a subset of Place.
- Supporting multiple styles. If we assume a artistic style is a function, then support multiple style will be like to make a neural network with many functions.
- Add GAN loss to improve quality
Reference
[1] Gatys, Leon A., Alexander S. Ecker, and Matthias Bethge. “A neural algorithm of artistic style.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1508.06576 (2015).
[2] Goodfellow, Ian, et al. “Generative adversarial nets.” Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2014.
[3] He, Kaiming, et al. “Deep residual learning for image recognition.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1512.03385 (2015).
[4] Im, Daniel Jiwoong, et al. “Generating images with recurrent adversarial networks.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1602.05110 (2016).
[5] Lee, Chen-Yu, et al. “Deeply-Supervised Nets.” AISTATS. Vol. 2. No. 3. 2015.
[6] Johnson, Justin, Alexandre Alahi, and Li Fei-Fei. “Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution.” arXiv preprint arXiv:1603.08155(2016).
